Treatments
TIPSS
TIPSS (Trans-Jugular Intra-Hepatic Porto Systemic Shunt)
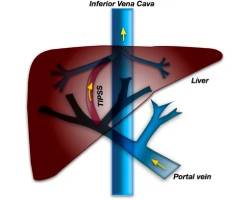
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a procedure to create new connections between two blood vessels in your liver. You may need this procedure if you have severe liver problems.
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt or TIPS is a procedure that uses imaging guidance to connect the portal vein to the hepatic vein in the liver. A small metal device called a stent is placed to keep the connection open and allow it to bring blood draining from the bowel back to the heart while avoiding the liver. TIPS may successfully reduce internal bleeding in the stomach and esophagus in patients with cirrhosis and may also reduce the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites).
What is a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS)?
A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is a tract created within the liver using x-ray guidance to connect two veins within the liver. The shunt is kept open by the placement of a small, tubular metal device commonly called a stent.
During a TIPS procedure, interventional radiologists use image guidance to make a tunnel through the liver to connect the portal vein (the vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver) to one of the hepatic veins (three veins that carry blood away from the liver back to the heart). A stent is then placed in this tunnel to keep the pathway open.
During a TIPS procedure, interventional radiologists use image guidance to make a tunnel through the liver to connect the portal vein (the vein that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver) to one of the hepatic veins (three veins that carry blood away from the liver back to the heart). A stent is then placed in this tunnel to keep the pathway open.
What are some common uses of the procedure?
A TIPS is used to treat the complications of portal hypertension, including:
- variceal bleeding, bleeding from any of the veins that normally drain the stomach, esophagus, or intestines into the liver.
- portal gastropathy, an engorgement of the veins in the wall of the stomach, which can cause severe bleeding.
- severe ascites (the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen) and/or hydrothorax (in the chest).
- Budd-Chiari syndrome, a blockage in one or more veins that carry blood from the liver back to the heart.